
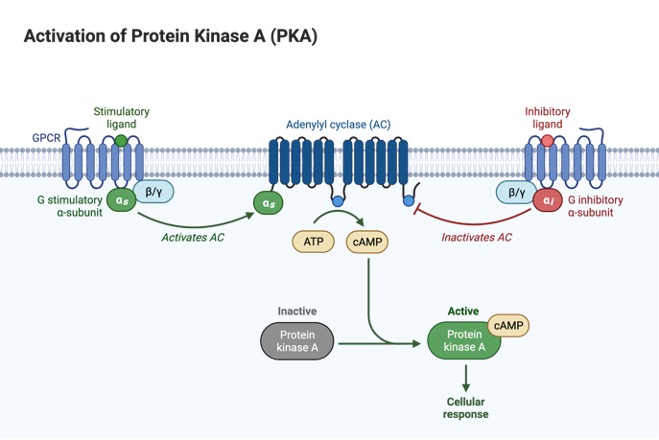
The downstream signaling of cAMP is mediated by its interactions with effector molecules, protein kinase A (PKA) or exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP (Epac), which have been shown to modulate phagocyte functions. PDE inhibitors prevent such degradation, resulting in accumulation of intracellular cAMP. Phosphodiesterases (PDEs), which degrade cAMP to AMP, are another regulator of intracellular cAMP levels. Pertussis toxin and cholera toxin cause elevated cAMP levels through ADP-ribosylation of either the Gαi subunit to prevent its inhibition of AC or of the Gαs subunit to constitutively activate AC, respectively. The production of cAMP is also regulated by microbial pathogens. The binding of the Gα subunit to adenylyl cyclase (AC) either stimulates (Gαs) or inhibits (Gαi) the enzyme's generation of cAMP. The binding of an agonist to the G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) induces a conformational change resulting in the liberation of the Gα subunit from the βγ subunit complex. The regulation of cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels and antimicrobial actions. By contrast, Gαi subunits inhibit AC and the production of cAMP some well-known Gαi-coupled GPCR ligands include chemokines CCR1–10 and CXCR1–6 as well as leukotrienes B 4, C 4, and D 4 ( 4). Some of the well-known Gαs-coupled GPCR ligands include epinephrine and norepinephrine, histamine, serotonin, and certain cycloxygenase (COX)-derived prostaglandins (particularly prostaglandin E 2 and I 2 ) ( 4).
#Define cyclic amp free#
The free Gαs subunit stimulates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase (AC) to catalyze the cyclization of ATP to generate cAMP and pyrophosphate ( 5, 6).
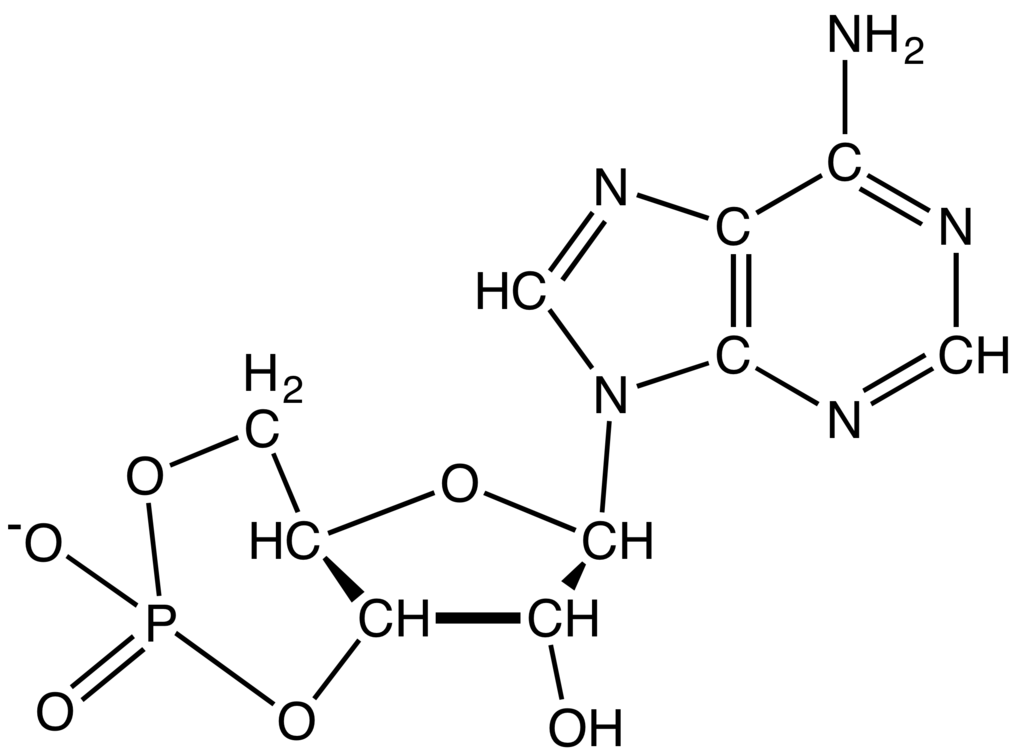
Ligand binding results in the exchange of GDP for GTP on the Gαs protein and its subsequent dissociation from the βγ subunit complex ( 4). The generation of cAMP is initiated when an extracellular first messenger (neurotransmitter, hormone, chemokine, lipid mediator, or drug) binds to a seven transmembrane–spanning G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to a stimulatory G protein α subunit (Gαs) ( Figure 1). Although many contemporary reviews on innate immunity focus on pathogen recognition receptors and signaling pathways ( 3), the importance of cAMP as a controller derives from its ability to exert broad modulatory effects that are independent of the pathogen, the recognition receptor, or the signaling pathway in question. This review will address cAMP regulation of innate immunity, with an emphasis on the lung. Biological processes mediated by this second messenger include memory, metabolism, gene regulation, and immune function ( 2). cAMP is now recognized as a universal regulator of cellular function in organisms including amoebas, plants, and humans ( 1).
Sutherland was awarded the 1971 Nobel Prize for this work, which would prove to be the first of five Nobel Prizes recognizing research on this molecule. Sutherland during his studies of the mechanisms of hormone action. The cyclic nucleotide cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-the original member of the family of second messengers-was discovered by Dr. The energy stored in ATP is then used directly or indirectly to drive all other cellular processes that require energy, of which there are four major types: (1) the transport of molecules and ions across cell membranes against concentration gradients, which maintains the internal environment of the cell and produces the membrane potential for the conduction of nerve impulses (2) the contraction of muscle fibers and other fibers producing the motion of cells (3) the synthesis of chemical compounds (4) the synthesis of other high-energy compounds.This review will provide clinicians with an overview of the cyclic AMP axis, its role as a down-regulator of host antimicrobial defense functions, and the clinical and translational relevance of such actions. The energy that is derived from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, or proteins is used to synthesize ATP. The bond between the phosphate groups in ADP or the two bonds between phosphate groups in ATP are called high-energy bonds, because hydrolysis of a high-energy bond provides a large amount of free energy that can be used to drive other processes that would not otherwise occur. Adenosine can be linked to a chain of one, two, or three phosphate groups to form adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), or adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Adenosine nucleotides are involved in the energy metabolism of all cells. It is a structural subunit of ribonucleic acid (RNA). a nucleoside composed of the pentose sugar d-ribose and adenine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
